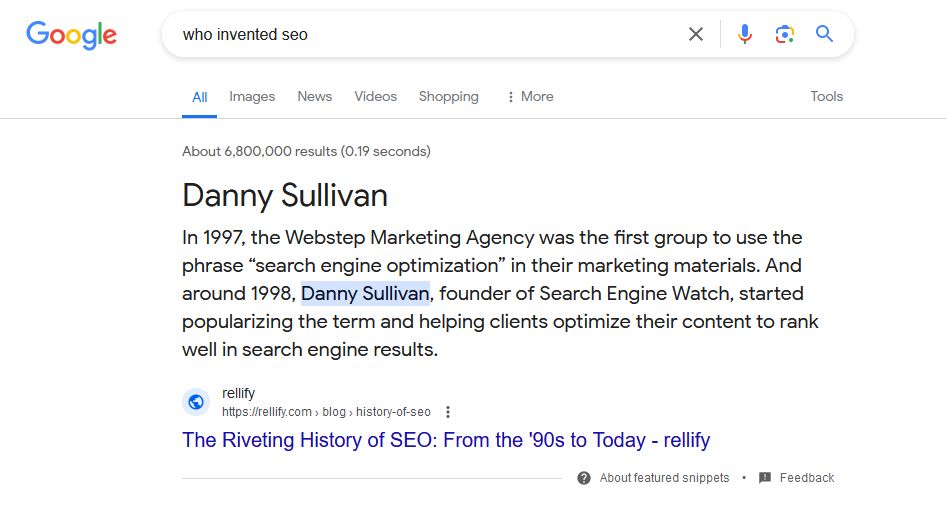
Who invented SEO?
5th April 2024, Google suggests that Danny Sullivan “invented SEO”… For context, Danny Sullivan is now Public Liaison for Search at Google.
Here is an AMA from Bruce Clay to and one of his answers suggesting he was already using this term in 1996…
“In 1996, I was one in a small but growing field of search engine-focused web developers who figured out that steps could be taken to improve a website’s position in search engine results. One problem we all faced was explaining to businesses what it was we could do. Some people were calling it “search engine ranking.”
I had a different perspective. In the mid-70s I worked at a mainframe performance measurement company, Boole & Babbage. We had products that optimized application programs and determined how a program could be modified to perform faster. If I could take an application that would run in an hour and I could make it run in 10 minutes, that was valuable because mainframe computer time was very expensive. So anything you could do to improve performance was great. This was called “program product optimization.”
When I got into work on websites I just started calling it “search engine optimization” – it seemed to me to be a natural term based upon my history. I had years of history “optimizing.”
The image itself claims that Danny was responsible for popularizing the term but not really inventing it..
Who invented the fidget spinner?
Ask Google Assistant and it will tell you that Catherine Hettinger did: a conclusion based on poorly-reported stories from The Guardian, The New York Times and other major news outlets.
Bloomberg’s Joshua Brustein clearly demonstrated that Ms. Hettinger did not invent the low friction toy. Nevertheless, ask Google Assistant “who really invented the fidget spinner?” and you’ll get the same answer: Catherine Hettinger.
The authority of these domains accrued over years has made it possible for them to rank higher. Their authority also inturn is used by Google to provide answers to questions in the Google search itself.
SEO makes it possible to both gain authority and establish yourself as the though leader in your field.
In this guide you will learn
- What is SEO and why is it important?
- How to do SEO?
- Anatomy of a search engine
- What is CTR?
- E-A-T
- Document Structure / OnPage SEO
- Tools Of The Trade
- Off Page SEO
- Measuring SEO success
What is SEO?
SEO is more than just about search results though.
If done right, it can bring in more sales, build brand awareness and increase your website’s conversion rate.
An effective SEO strategy not only helps your site rank well in search results but also improves your business prominence online.
SEO is a continuous improvement process.
Often, the real questions are about usability: What makes it hard for search engines and your users to navigate through your site and find the right information?
A user-friendly website sustains users.
Plenty of factors affect your search engine rankings, and one of the most critical factors is user experience.
In a Pubcon in 2010, Matt cutts then head of webspam said that Google had over 200 signals and many of them have 50 variations in the single factor alone.
Backlinks are the single most high impact factor in Google rankings.
If I have lost you already, you probably won’t enjoy what I am about to say in this guide.
However, if you are open to the idea then read on..
About The Author
Before we jump into the guide itself, a bit about me. I am a trained Robotics engineer, a professional hacker, a stand up comedian and an entrepreneur. I was in the team that helped improve the landing gear for the Mars Rover.
I’ve hacked Salesforce, Slack, Servicenow, Dropbox, Google and have been recognized for it. I’ve run an agency for 13 years and founded it just when the global financial crisis was unleashing on the financial markets at the age of 24.
I speak 4 languages fluently (more on that later) and have hundreds and thousands of failures each culminating into massive successes.
As an engineer, I’ve been trained to solve problems using experimentation. As a hacker, I often write tools that help others solve problems. As an entrepreneur, I have survived two global recessions and have put up steady growth in our business every year.
This guide is a compilation of what I’ve learned through many failures. It has been 15 years in the making. This denomination is important because the more experiences you have in the world of SEO, the more ways you have on how to solve the ranking puzzle.
Skip reading the guide and get all of it implemented via our SEO services.
There are two things that will help you rank in search engines
- Document structure
- Backlinks
In the SEO world, improving document structure is also termed as Onpage SEO. The things that you do to improve your rankings outside your website is called Off-page SEO. Acquiring backlinks is a major part of Off-page SEO.
This is not to say that you cannot increase your traffic via content strategy alone. You can. You can exponentially increase your traffic by acquiring backlinks along with a content strategy. Consider content as the engine of your car. Backlinks as the turbo booster required to win the race.
Motivations
Consider the motivations behind why we do things ? Consider the author’s motivation behind writing this guide. Consider Google’s motivation when laying out guidelines to improve your page.
Google recommends certain best practices to improve your page structure. Google does this because its motivation is to crawl your website with ease. It wants to avoid spam and/or low quality results. It doesn’t want you to “game the system”. Therefore its recommendations may not always align with what you should or should not do on your website.
For instance, there is conflicting advice on backlinks from a number of sources in Google. Its official position is that it asks you to not engage in acquiring backlinks.
However, Xooglers ( ex Googlers ) that do startups focus on acquiring backlinks as their priority. A famous example that comes to mind is the company Shoes of Prey.
This guide balances this view and does NOT always agree with Google’s guidelines. However, it does make this distinction in the guide wherever necessary.
How to do SEO?
You will often hear SEOs say that nobody can guarantee you #1 position on Google.
They will say that if somebody guarantees you #1 position on Google they are lying.
They are fly by night charlatans that do not understand how search engines work. It’s not an axiom.
I am about to tell you how you can rank #1 on Google or any other search engines.
Google is a search engine whose rankings are machine generated.
There is no manual intervention in how pages rank.
Google sometimes intervenes manually via applying penalties to websites. You will not get a penalty if you follow the recommendations defined in this guide.
With experimentation, you can see how Google’s search behaves and adjust your strategy to get to the position #1. It’s not rocket science. Its basic experimentation and iteration.
Out of all the changes the Google algorithm has undergone in recent years, none is more apparent than the shift away from keyword-dense content in exchange for a greater focus on relevant, well-written content.
This has been a longstanding goal of search engine algorithms, and it is abundantly clear that the algorithms are succeeding in generating search results based primarily on the relevance as well as the overall quality of the content.
Despite a general understanding of the meaning of terms like “relevance” and “quality,” it is still necessary to more precisely define each one as it relates to search engine optimization.
In most cases, a search engine is more likely to yield results favoring the most in-depth and all-encompassing content relevant to the search term.
Of course, this is only true if the in-depth and all-encompassing content is written well and organized within the confines of a clear, overarching structure.
Now before we start optimizing your site let’s discuss some fundamentals of how Google search works.
Anatomy of a search engine
Search for “GM” and the Gmail homepage ranks prominently.
Is Google pushing its own products on people? Well, yes, but not in this case. This is an example of a query refinement algorithm at work. A QDF (query deserves freshness) algorithm altered the search results to provide for popularity over accuracy. Google is altering its results in recognition of the fact that many people who search “gm” subsequently search for “gmail.”
Let’s start with the most obvious – Google’s mission.
Google wants its audience to have access to the most relevant information as quickly as possible. Google wants to do this by giving you the information on Google itself.
If you never leave Google, Google can make more money. But there’s more.
Buried under is the fact that Google makes money when users click. No click, no money. This includes when users click on organic results. The single most important factor for Google is click through rate (CTR).
The #1 result on Google has ~25% CTR.
What is CTR?
Let’s look at a typical search listing from the search engine result pages (SERPs)..
A user on a Google search results sees
- Title – The text in blue.
- Description/Snippet – 2-3 lines text directly below the title.
- URL – Immediately above the title.
- Sitelinks – Enhances the results by adding supplemental links below the description text
Sitelinks only show some of the times, the listing comprises three immutable properties:- the title (blue text) , the URL & the description (2-3 lines of black text).
- A high CTR is a very good indication of your listings appeal. A lower CTR demands that the listing be improved.
- You don’t need to make your listings clickbaity to get a higher CTR. Some of the most mundane titles have a higher CTR because of the fact that they directly address the user’s search query. However, it is undeniable that the clickiness of a title is important to get the user to the page.
We now arrive at what is essentially a catch-22
- In order to get the users to click through to your results you need a catchy title & description that may not be descriptive of the page. This may reduce its relevance to the topic.
- In order to rank higher on search engines so that your users can see you, you will need descriptive title and description. This takes the “clickiness” out of the title and description.
So how do we fix this ?
We focus on the document structure of the page to improve its relevance but allow for some artistic freedom in choosing titles and descriptions.
We fix any subsequent authority loss of the page by acquiring backlinks.
- Good conversion rate: A complete guide to conversion rates.
- Speed analysis: Page speed analysis of top 25K sites.
- Conversion Rate Optimization
Let’s understand four main points before you go deeper into how to rank for specific keywords.
E-A-T
E-A-T means Expertise, Authoritativeness, and Trustworthiness.
It has been a part of Google algorithm for well over a year.
It is even referenced in the Google search quality evaluator’s guide.
MC refers to main content.
One way of establishing expertise and authority is to write indepth content.
Prove expertise using long form of content.
Usually 2500 words plus.
Show trustworthiness by getting inbound links.
Topics & Keywords
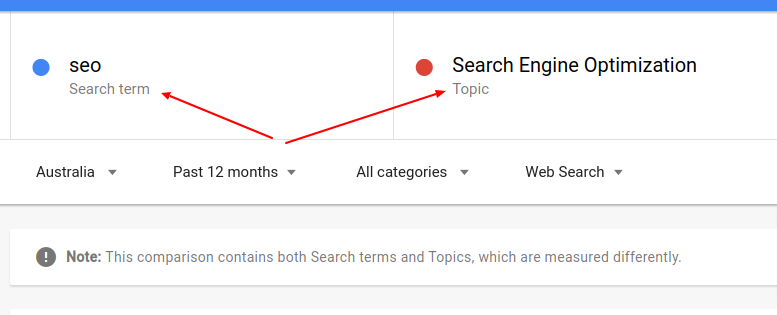
Keywords are different than topics. Google treats them so. SEO is a keyword while search engine optimization is a topic.
How do we know ? Use Google trends.
Keyword or Topic Specificity
Consider the search results before you target a page for a set of keywords.
A great example is the term SEO.
When you search for the term SEO, results show “guides” that show you how to do SEO.
It doesn’t show results with commercial intent like companies providing SEO services.
This is because the word SEO is broad. Google through data believe that people that look for the term “SEO” are actually looking for guides on how SEO works.
While you may be able to get to the first page with lack of comeptitors, position one is going to be difficult without keword specificity.
Content is still king
If you are an expert in the field there is no other way to please your potential clients like content.
Both Google and your potential client will love your indepth content.
It also demonstrates E-A-T.
Invest in an extensive content strategy. It will make it easy to rank number one for whiever keyword you desire.
Now before we jump into how we optimize our pages, let’s talk about how to pick the right words to rank for. In the world of SEO, we call this keyword research.
Let’s quickly learn how to check your what Google has and has not indexed.
This is checking our site pages vs what Google has in their database.
There are two ways of basically checking Google’s index. You could either submit your site to Google search console (See the complete guide here) or you could use the site command.
Try the following Google search and replace “example.com” with your site URL.
site:example.comWhat you see is all the URL that Google has in their index.
Now before you start changing the pages Google already has in their index, let’s discuss some fundamentals.
Namely, keyword research.
There are a number of ways of doing keyword research and some would argue that spending a very large time on keyword research leads to a larger ROI. While this argument has merits, it isn’t warranted the first, second or the third iteration of your keyword research.
We will talk about in-depth keyword research for those instances in the future but for the purposes of this guide, I will show you the most foolproof way of researching keywords.
Keyword research
Read the beginner’s guide to keyword research
Let’s talk about the onpage SEO.
Document Structure / On-Page SEO.
Consider the following elements when thinking about document structure.
- URL slug
- H1-H6 tags.
- Titles
- Meta description
- Responsiveness (mobile-friendly)
- Readability
- Paragraph text
- Bold, Italics & underlined text
- Internal links
- Media
- Structured data
- Recency ( dates )
- Crawler directives
In addition to the above, there are things that you can do to improve the crawlability of this document that include factors such as
- Sitemaps
- Robots.txt
- Security vis SSL certificates
- Site structure such as broken links, permanent redirects, page not found and server errors
- Page speed
- Domain authority
- Page authority
A page may have other elements to enhance its authority and visual hierarchy but these are irrefutably the most common.
These factors are enough to rank you on page 1. Once you are on page 1, your journey to #1 is going to be difficult but not impossible. Getting to page 1 is like losing the first few kilos when starting to exercise. You lose water weight fast and it is noticeable. The real journey is in losing the last 10 kilos.
The following describes how to do your landing page to rank for a cluster of words.
Let’s dive into each of the factors responsible for rankings.
URL slug
The part of the URL that identifies the page is called the URL slug. A url slug may have parent pages or categories directly above it.
In the following example, the word “seo” is the url slug.
mojodojo.io/seo/
This URL is also called a friendly URL. This is because it does not have any query parameters or dynamic text.
A friendly URL is also a recipe for higher type in traffic. The following are some best practices with URL structure
- It helps Google understand what the page is about
- It helps the visitor know what the page is about.
Furthermore, a user is more likely to click links with human-readable slug. The friendly URL slug serves as a check against the anchor text manipulation.
- Keep your URLs short
- Use a primary keyword in the URL slug
- Avoid keyword stuffing the URL
- Use a logical parent/child relationship
- Avoid dynamic URL or query parameters
- Make your URL available only on one version of the site (www vs non www)
- Avoid stop words in the URL
- Use canonicalization
All things being equal, short URLs have a higher CTR than longer URLs. When all other factors are equal, a relevancy score can be won by having additional semantic value in the URL.
H1 tag
One of our favorite extensions that helps understand a document better is Web Developer. (Chrome, Firefox)
Using this tool, you can pull up the document outline of any page.
After installing, simply head to the page you wish to document outline, click the extension > Information > View Document Outline.
Here is a document outline of the Wikipedia SEO page.
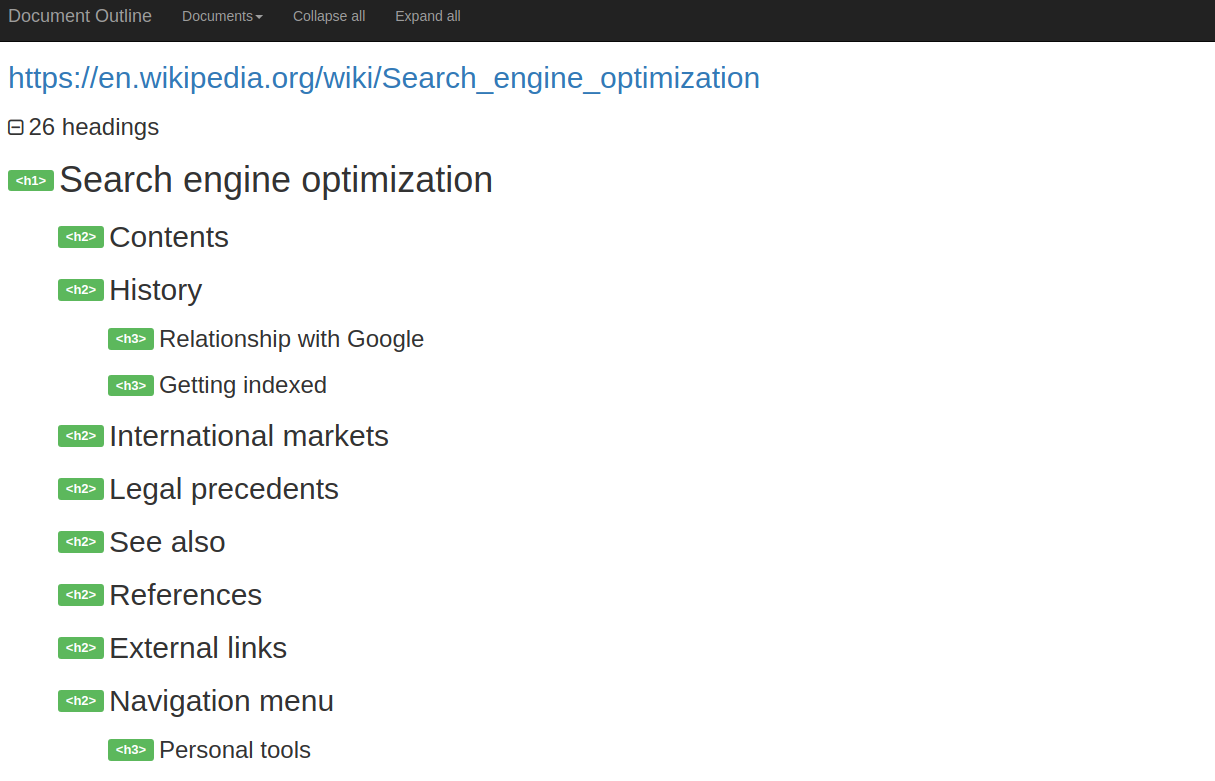
Note how the H1 is titled. It matches exactly with what the page is about. H1 hence is the most critical element of the page usually reserved for titles.
The best practices around H1 are
- Use only one H1 tag on the page.
- Your H1 tag should be the title of your page
- H1 tag should fulfill the user’s expectations
- Use the title case for H1 because this will likely be your search results title.
- Your title tag and your H1 should match
- Include your primary keyword in the H1
Titles
So how does Google and other search engines decide what title and description to show for each page ?
Google says that it uses a number of different sources to determine the best title for the query but also provides you the webmaster with a way to indicate your preference.
Usually, if you write a clear & concise title, Google tends to respect your title.
The best practices for indicating your preferences of the title are
- Use the <title> element in the <head> to indicate your title preference in the document structure.
- Write a title that is descriptive and concise. Avoid overdoing the titles by stuffing as many keywords as possible. Keyword stuffing also generally leads to a poor CTR.
- If you have a javascript based site, have it as high in the head as possible. Even better, avoid javascript based sites and opt for static sites.
Google considers some of the following to choose which title to show
- <title>
- H1 of your document
- H2-H6 if the primary H1 is less relevant
- Other content in the body of the page
- Other text contained in the page
- Anchor text on the page
- Anchor text of links pointing to the page
Google starts rewriting titles when you have a) over optimized b) stuffed with keywords c) repetitive titles across the site d) to match the user’s query and improve CTR.
Google only displays 50 to 60 characters of a page’s title tag. For maximum visibility, it’s recommended that you follow this guidance by keeping your pages’ title tags under 60 characters.
Snippet/Description
A snippet or a description also influences your CTR like the title. It is shown in the summary part of the search results and users often use that to make a decision on whether the page will answer their query.
Google generally uses the meta description tag on the page to determine the most appropriate snippet to show on the result pages. Google will also consider structured data of the page to determine the best fit (more on this later).However, it will show different snippets based on a number of factors such as
- Keyword stuffing the description tag.
- Repetitive description tag across the site
- Generalizes the concept but doesn’t summarize the page.
- Either too short or too long.
The best practice to write great meta descriptions to show on the Google search snippets are
- Create a unique description for each page of the site.
- Include and topicalize each description to the theme of the page
- Use attributes in the description like titles, prices, ingredients and so on.
- Use Active Voice with Action Oriented Signals.
Google displayed no more than 155 characters of a page’s meta description in its listing. In 2017, Google increased the length of meta descriptions to 300 characters. You can technically create meta descriptions of any length, but Google will truncate them if they are longer than 300 characters.
Consider writing your meta descriptions as an AD or a tweet. Essentially, you are looking at writing a highly engaging tweet that could potentially be seen by millions of people and has to have the power to draw them in to learn more about what you are offering.
The core of a meta description centers on good salesmanship, as you are essentially creating an advertisement that is meant to appeal to potential customers. Therefore, you want your meta description to clearly state your intentions in a way that combines direct marketing with some creative flair.
H2 & H3 tags
H2 usually carry secondary topics or break the main topic into multiple branches. H3 are used to further break down a specific H2 into more topics.
We use H2 & H3 to insert additional long tail keywords.
Responsiveness (mobile-friendly)
Your website should be mobile first. This means, you should design for a mobile phone before you design your desktop version.
Mobile phones have a smaller viewport and can often result in a skimmed version of your main page. It is likely that you may be in a handful of industries where users use your desktop site more than mobile.
You would notice that your mobile traffic continues to increase and will do so in the future.
Even Google has switched to a mobile crawler in the past few years. You can confirm this via the Google search console.
Body text
The body text usually found in <p> tags is the core of the body. Generally the larger the body, the more specific the text is.
Google generally will value your pages lower if they all have low volume content. There is no one size fits all rule of thumb. However, in my experience sites with an average of 1000 words per page fare 70% times better than those with 500 words per page.
The distinction is clear. Write detailed, quality & lengthy content.
Bold, italics & underline
I would recommend avoiding bold , italics and underlined text altogether. These provide no SEO benefits and may reduce readability if not done properly. You can read about that in the practical typography book.
Internal links
Search engines will follow internal links, guiding them to other pages that they may haven’t discovered. They also use the text of that link ( anchor text ) to determine what that link is about. Internal links are very useful in improving the authority of pages being linked to.
Consider the rankings of Wikipedia. Wikipedia shows up for any search terms on Google usually at number 3 or 4 positions. It also occupies number #1 position for a lot of long tail keywords.
The number 1 reason for Wikipedia to be able to rank that high is internal links. Wikipedia is perhaps the extreme enactment of internal linking.
Here is a page about SEO on wikipedia. Note the number of internal links.
The best practices for internal links are
- Link internally and link often.
- Use the right anchor text for linking
- Color the link appropriately to denote the difference
Media
Visual search engine technology has improved. Search engine crawlers have come a long way, and while images can be identified, crawlers still provide preference to keywords in an alt tag.
The text associated with the image helps the crawler relate it to the rest of the content of your website.
How do you choose the format of the image ? How to title it ?
Put simply, if it’s an illustration, use PNG, if it’s a photo, use JPEG. Output the image at the right size. Oftentimes, I see scaled images on websites shown in 300PX with the actual image being 2000PX or more.
Some folks argue that WEBP is better than JPEGs. Jyrki Alakuijala, one of the creators of WebP, on WebP vs JPEG:
- For high quality photography, I (and butteraugli) believe that JPEG is actually better than WebP.
- Below JPEG quality 77 WebP lossy wins, above JPEG quality 77 JPEG wins (for photography).
- This was based on the maximum compression artifact in an image — averaging from 1000 images.
However, in defense of WEBP, they also support transparency and animation.
From Chrome 76 and Firefox 74, you can use the loading attribute to lazy-load images without the need to write custom lazy-loading code or use a separate JavaScript library.
Use the loading attribute to completely defer the loading of offscreen images that can be reached by scrolling:
<img src=”image.png” loading=”lazy” alt=”…” width=”200″ height=”200″>
Best practice for image optimization are
- Name your images in plain language
- Use keywords in description and titles
- Optimize alt attributes to have an impact, don’t keyword stuff
- Choose image dimensions wisely to fit the element on your page
- Reduce the size of all images to make your page load faster
- Pick the right file types like JPEG for better quality
- Improve JPEG quality using web and devices format
- Optimize your thumbnail images for social media sites using OGP
- Use image sitemaps to better inform search engine crawlers
- Don’t place multiple images on a page or blog post unless each provides impact
- Test your image optimization through sites like Screaming Frog and Xenu
- Lazy load your images and videos
Descriptive, keyword-filled file names are important to helping search engine crawlers understand what’s in the photo. This borrows from the concept of friendly URLs.
If the crawler can understand the subject matter of the image, it can quickly determine how relevant your content is to certain queries being searched by users.
Your filename may be “IMG_722011.JPEG,” so change your image filenames to reflect what they are about. For example, an image about a wedding in Melbourne on a beach might look like “Melbourne_Beach_Wedding_2018” when it is renamed. This helps provide more SEO value to your images inherently.
You wouldn’t want to use “wedding-1.jpg” or “wedding-2018” as these are generic.
Structured data
At a Google IO conference, a session titled “How to Stand Out in Search with Structured Data” revealed that in several case studies, the sites showed up first because of their schema data implementation. In fact, some interesting numbers that were shown are
- 25 percent higher CTR on pages with markup.
- 35 percent increase in visits for recipes with markup.
- 1.5 percent increase in more time spent on pages and 3.6x higher interaction rates.
- 82 percent increase in CTR for rich snippet results.
- 20 percent increase in clicks for pages with schema markup.
Schema markup also called structured data is essentially a form of microdata embedded into a webpage. It helps Google and other search engines better understand attributes of the object the page represents.
An example would be a product page that may have attributes like title,description,price,SKU number, color, size and so on..
You can find all available types of schema at Schema.org.
How to add schema is beyond the scope of this guide. You can use an extension if you are using a popular CMS like WordPress.
It is highly recommended that you identify any type of pages that you can markup with schema. Implementing schema is a very high ROI activity for the purposes of SEO.
Recency (dates)
We saw an example of QDF ( query deserves freshness ) at the top. If at the start of the new year, you update the content on your website, you should show a “modified date” timestamp instead of the “published date”. This serves two purposes
- It helps search engines understand that the content has been updated.
- It helps you rank better as now your content has been recently updated (freshness).
SEOs will abuse this often. You can note this by seeing the year (2022 or 2023) used in the title of the guide.
While Google has smartened up to this abuse, it still works in 2022. Google does take a diff of the page though. So if you are going to do this, make sure you also update a portion of the content.
You should also use this if your user is explicitly searching for a year in their query.
Crawler directives
Google and other search engines understand a number of directives under the meta tag.
A good example of a directive that you can include in the page is
<meta name=”robots” content=”noindex,nofollow”>
This explicitly tells Google to not index the page and not follow it either.
The main parameters that you could pass are
| All | index, follow |
| Follow | Crawlers should follow all links and pass link equity to the pages |
| Nofollow | Search engines should not pass any equity to linked-to pages |
| Index | Crawlers should index the page |
| Noindex | Crawlers should not index a page |
| Noimageindex | Crawlers should not index any images on a page |
| Max-snippet | Sets the maximum number of characters as a textual snippet for search results |
| None | Shortcut for noindex, nofollow |
| Nocache | Search engines shouldn’t show cached links for this page when it appears in search results |
| Nosnippet | Search engines shouldn’t show a snippet of the page (like a meta description) in the search results |
| Unavailable_after | Search engines shouldn’t index a page after the set date |
I would recommend not adding any meta name “robots” to your pages if there is no requirement to hide a specific part of your page.
You could give the same directives via the Robots.txt as well. More on that a bit later.
Content Pruning
“Content pruning” is an effective SEO tactic on large, established websites. It may benefit smaller websites too but the results are marginal.
Rather than archiving old content with historical significance, many websites will delete it from their servers and return a 410 status code. Gone.
They may also use a 301 permanent redirect to redirect the user to a more relevant page.
There are advantages and disadvantages to both these approaches. A more common tactic now is to use a 301 permanent redirect back to the homepage.
The goal is to optimize “crawl budget,” keeping Google focused on the content that matters now.
De-optimisation
De-optimisation is used to rank your target page for a specific topic instead of the one Google is ranking. Google sometimes ranks pages that have nothing to do with the topic based on anchor text from external links.
The way to de-optimise your page is to do the following:
- Merge similar pages so as not to depreciate a wrongly ranked page when it contains valuable information.
- Canonicalize, which is informing search engines of the more important page when there are pages that are almost identical. This action can prevent keyword cannibalisation from happening to you.
- Having No-index (use the robots meta tag to no-index specific pages ) can be helpful when you have pages that are important, but rankings for them are not needed.
- Delete pages that have thin content and take traffic from pages that are similar, but better.
Having done the above, you are almost ready to rank on page #1. There are some things that you should also consider.
Robots.txt
Robots.txt is a robots file in the root of your website that serves as a request to search engines.
Note that search engines may or may not follow the suggestions on this file.
A more specific way to deny Google or other search engines is to use the Robots directive on the page.
- Name the robots.txt file “robots.txt.”
- It’s important to make the robots.txt file accessible by placing it in your site’s top-level directory
- Be careful when you change your robots.txt file–this can block vast portions of your site from search engines.
- Don’t use the crawl-delay directive unless you need to (i.e. if you have a large site with a lot of visitors)
- Subdomains within a single site each require their robots.txt file
Some key things about Robots.txt to keep in mind
- User-agent: The search engine “bot” you’re giving directions to
- Disallow: The command that tells the bot not to crawl a given page or subset of pages
- Allow: Allowing the bot to index the page, showing it (and a description) on the search engine
- Noindex: Tells the bot not to index the page or subset of pages.
- Crawl-delay: A directive for the search engine to wait a given number of milliseconds before loading/crawling a page.
You can also use robots.txt to eliminate the redundancies posed by duplicate pages and other subcategories and folders within your site that carry plenty of URLs, but not much valuable information.
Sitemaps: You should create a sitemap of your site. This is usually in XML format. Popular CMS will create one for you out of the box or have extensions to do that. You can then use these sitemaps to submit to Google via the Google search console. Google usually looks at sitemap to discover new pages.
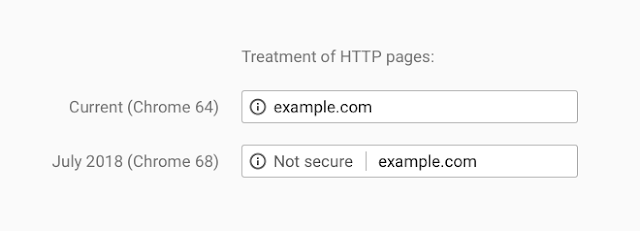
Security via SSL certificates: Ensure you have an SSL certificate installed. Letsencrypt is free. Modern browser like Chrome and Firefox now display a grey padlock for SSL encrypted sites. However, they now display a not secure sign for websites with no SSL certificate.
Site structure such as broken links, permanent redirects, page not found and server errors: Broken links should be redirected to the homepage or the most relevant page. Use a 301 permanent redirect. Your Google search console will complain at all the errors that your website has and you can use that to guide your work. Keep on top of Google search console errors.
Page speed: This is an absolutely critical component of ranking. If the site is slow, Google cannot crawl it. Page speed is a ranking factor so paying attention is crucial.
Domain authority & Page authority – While there are a lot of third party tools like SEMRush, Majestic, Moz, Ahrefs that give you this information, they all have their own algorithm to arrive at it. In my opinion, you should not focus on their numbers but work on getting inbound links.
SEO audit: Aim to audit your site or individual money pages every few months if there is a difference in your position or traffic you received organically.
Tools Of The Trade
There are plenty of tools on the market and I would recommend none of these.
Tools can be used to augment information or alert you to issues. However, you can still rank and do a great job without ever touching one of these tools.
I use screamingfrog on larger sites to detect issues in crawling. I do not recommend using tools to look at your competitors’ backlinks. Instead I would recommend focusing on acquiring new links.
Here are some tools in our industry that people use. The only one I use is Screamingfrog.
- ScreamingFrog
- Ahrefs
- Moz
- SEMRush
- Web developer chrome extensions (swiss knife of SEO)
There are obviously more tools but these are the most common amongst our industry.
Backlinks / Offpage SEO
Links are the currency of the web.
Without them, search engines couldn’t judge the relative worth of one page versus another.
Unfortunately, many large websites hoard their link equity by refusing to link to external websites, or, by using a rel=”nofollow” attribute on every external link (i.e. telling search engines to ignore those links). This makes the entire web poorer as a result.
This is also a directive Google has given so as to deter people from gaming the system.
This guide is intentionally short on this section. You will need to find trusted sources that can build links for you.
A lot of companies will build links via PBN ( private blog network )
This is damaging in the long run as the value of these sites is low and your domain authority will suffer.
Ask us about our link building process by getting in touch with us.
Measuring Success
We measure SEO campaign success using a number of useful metrics.
However, you should measure yours by the one thing that matters most. Revenue.
We track the following long term
- Keyword rankings
- Visitors loyalty/recency
- Sales / Leads
In addition to the above there are some secondary metrics you can track long term.
These include
- Lifetime value of a customer
- Bounce rate over time
- New visitors
- Domain authority